变量
python中的变量是不需要写出具体类型的,直接根据数据类型赋予变量,形如:
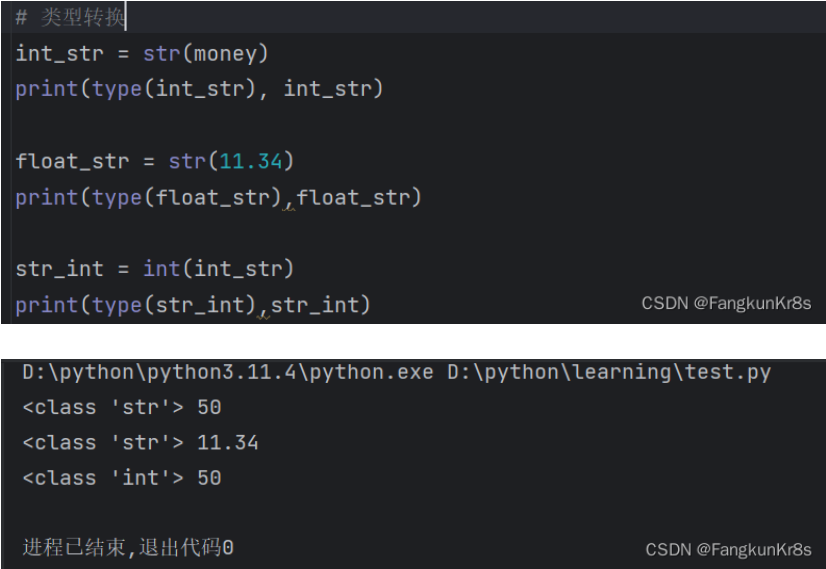
money = 50数据类型的转换
使用形如int(x),float(x),str(x)的形式来将数据类型转换:
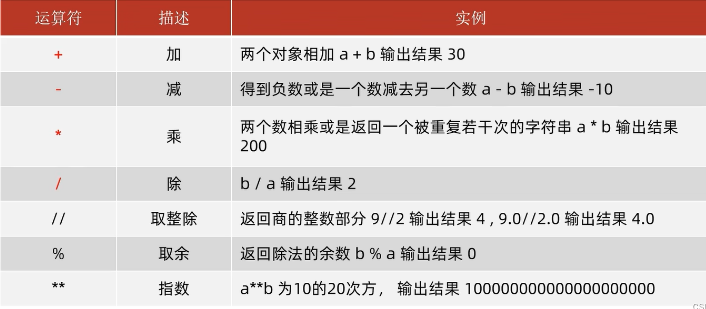
运算符
特别注意,取整除是//,求指数是**
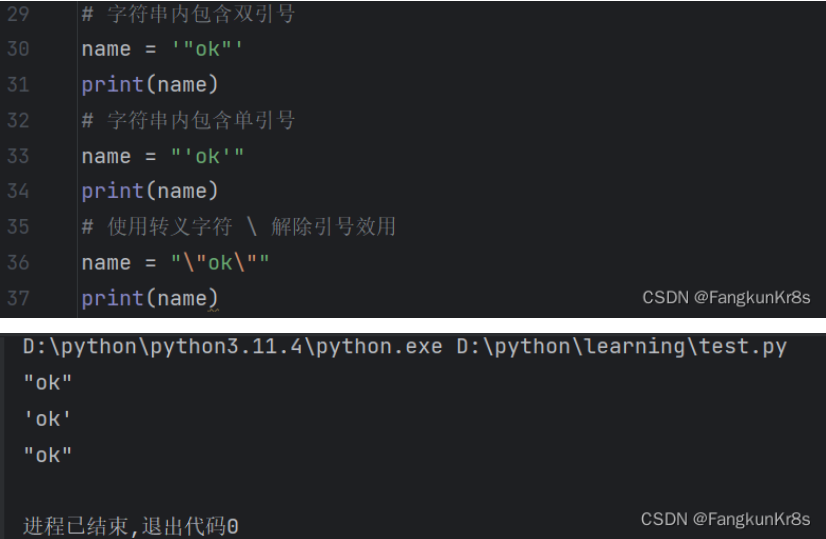
字符串的引号嵌套

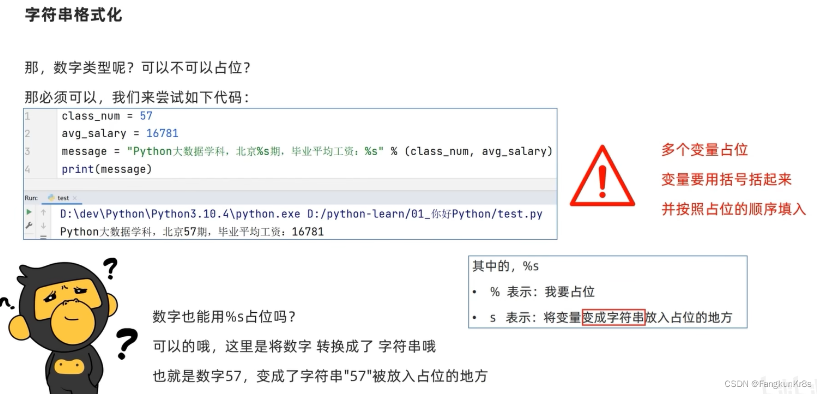
字符串格式化
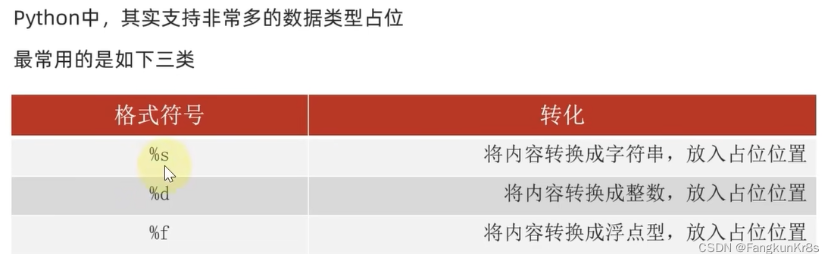
占位
字符串可以用%s的格式进行占位拼接
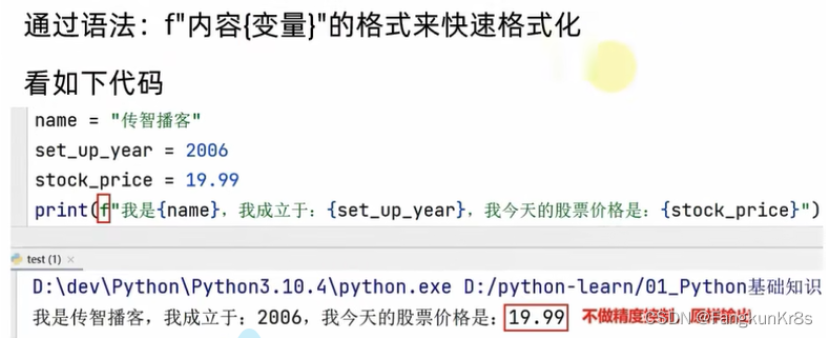
快速写法
快速格式化适合:1.不理会类型 2.不做精度控制,所以适合没有精度要求时快速使用
if语句

此外还有elif和else
for循环

函数
函数的定义:
def function():
函数体
return 返回值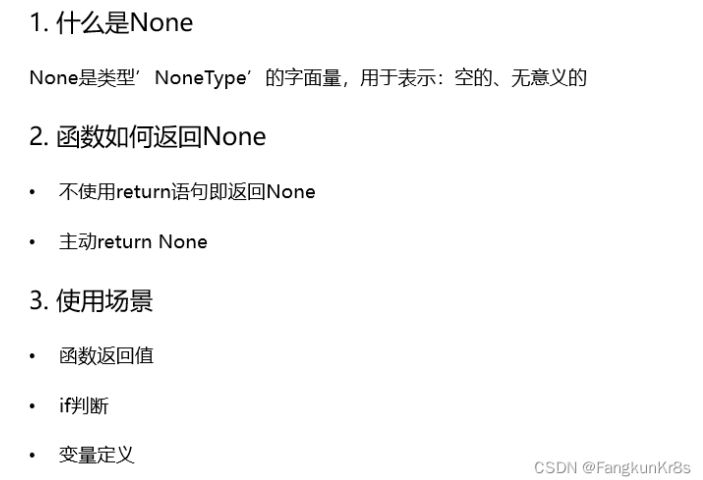

容器
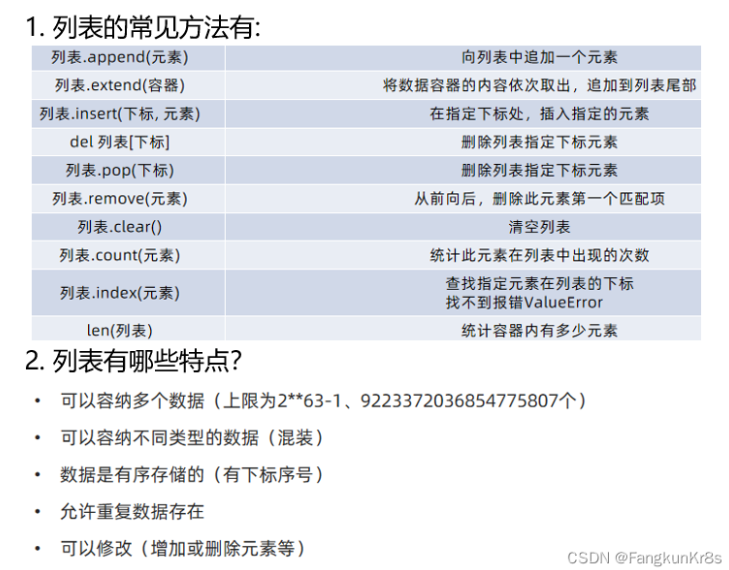
列表list

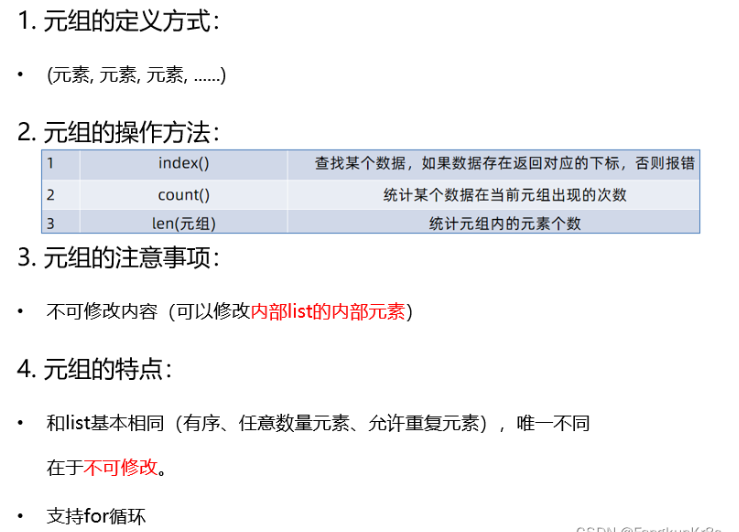
元组Tuple
字符串

切片

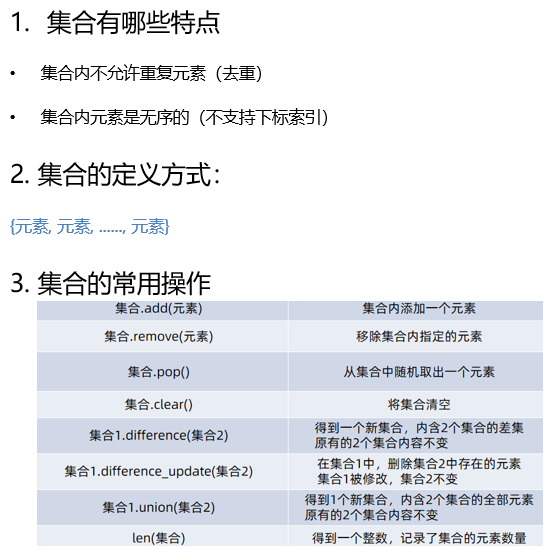
集合

字典


总结


函数的多返回值

函数的多种传参方式
关键字参数

缺省参数

不定长参数



匿名函数

例如:
def test(compute):
result = compute(1, 2)
print(f"结果是:{result}")
test(lambda x, y : x + y)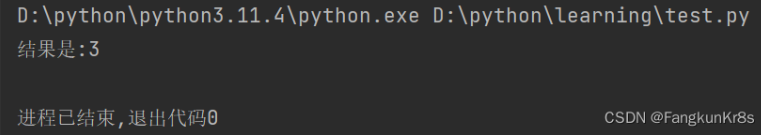
文件操作
读
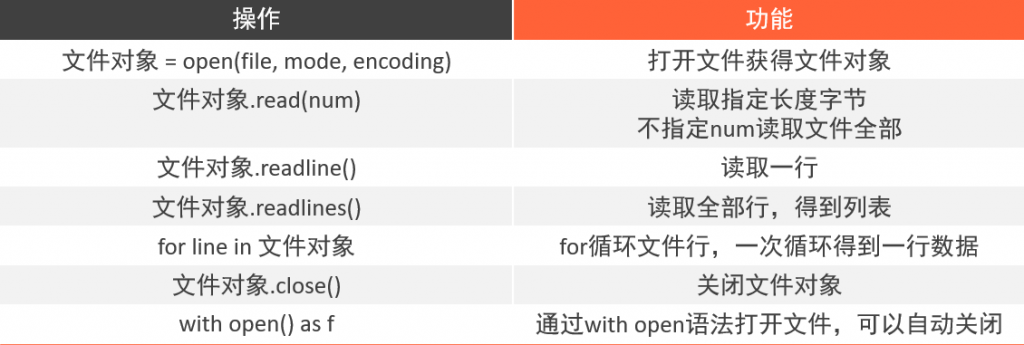

写

追加

异常的捕获方法
捕获常规异常
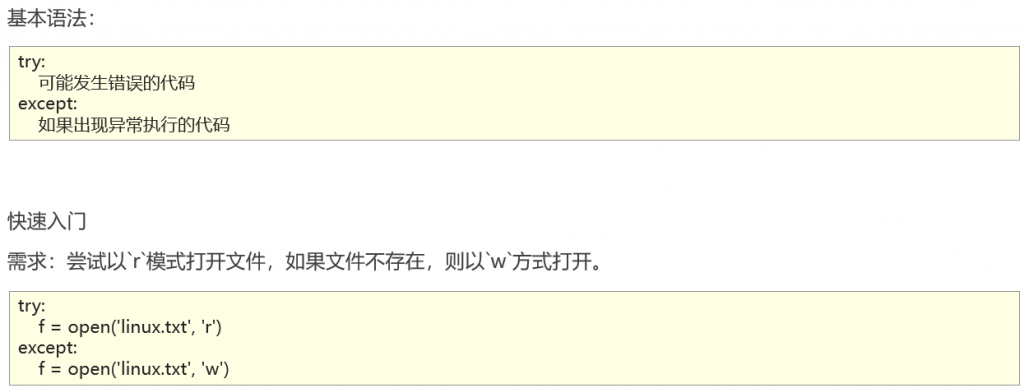
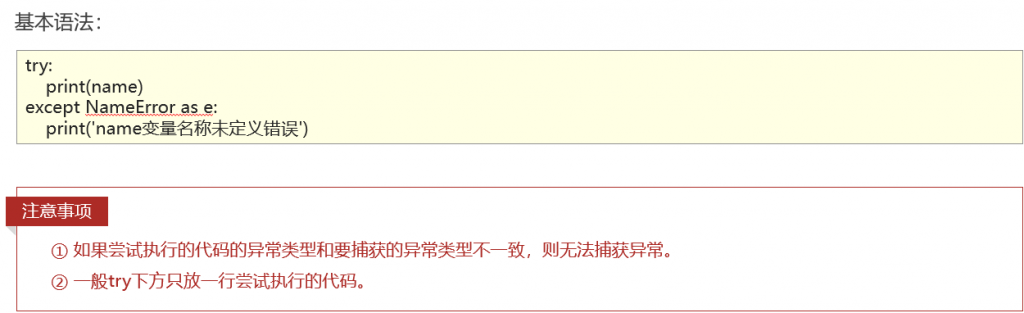
捕获指定异常
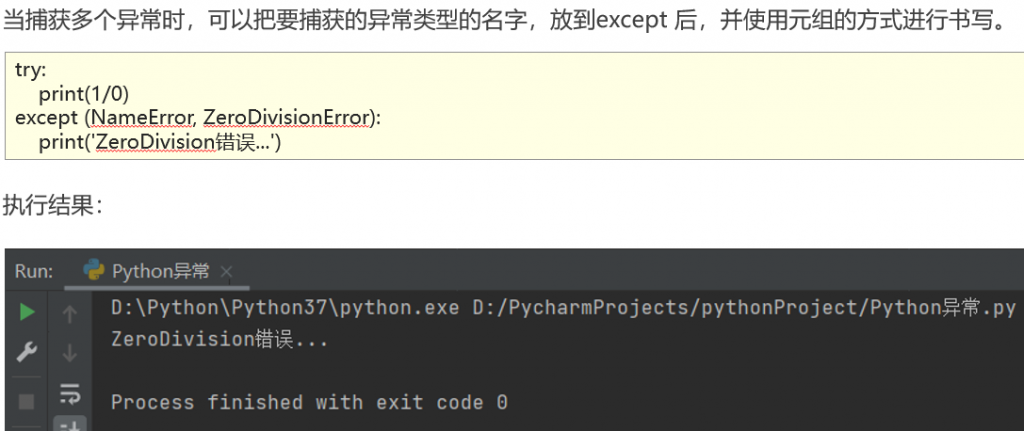
捕获多个异常
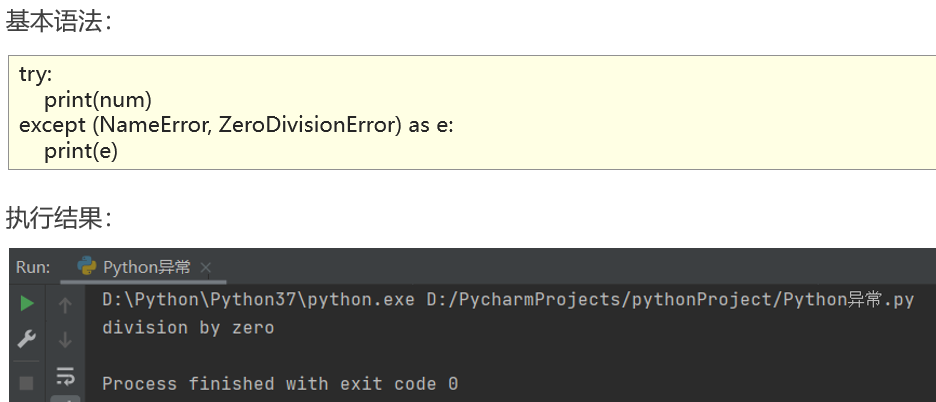
捕获异常并输出描述信息
捕获所有异常
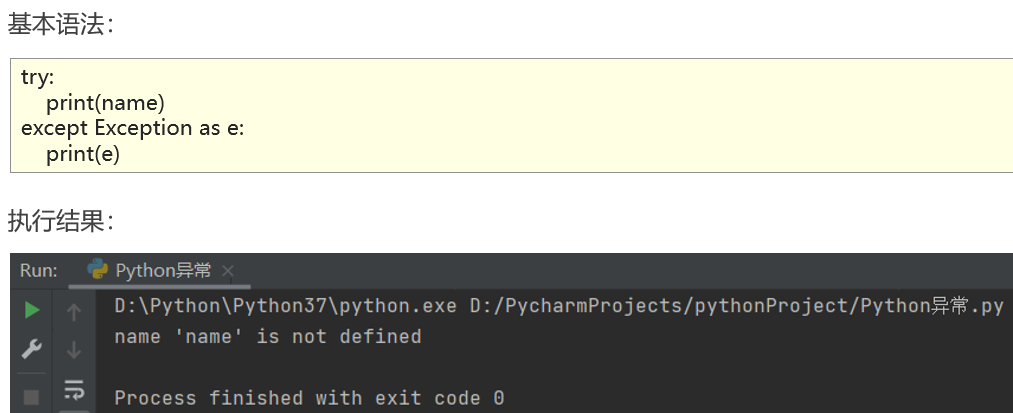
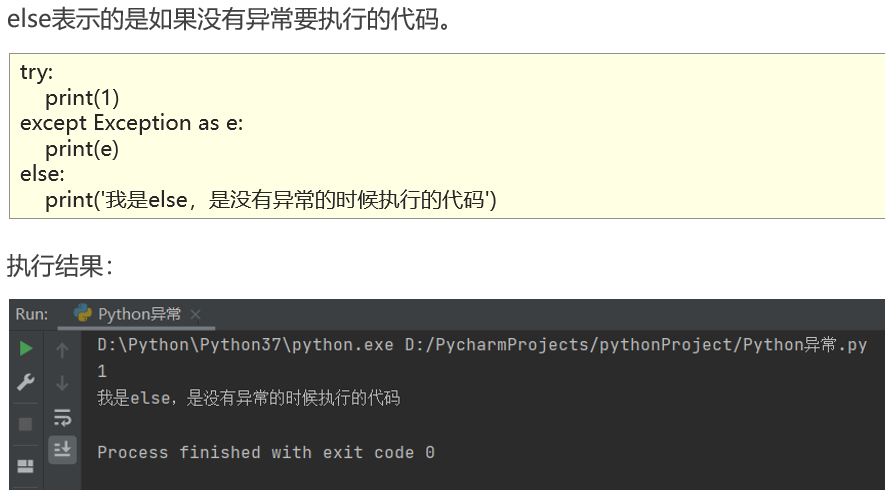
异常else
异常finally

异常的传递性
当函数func01中发生异常, 并且没有捕获处理这个异常的时候, 异常会传递到函数func02, 当func02也没有捕获处理这个异常的时候main函数会捕获这个异常, 这就是异常的传递性.

Python模块
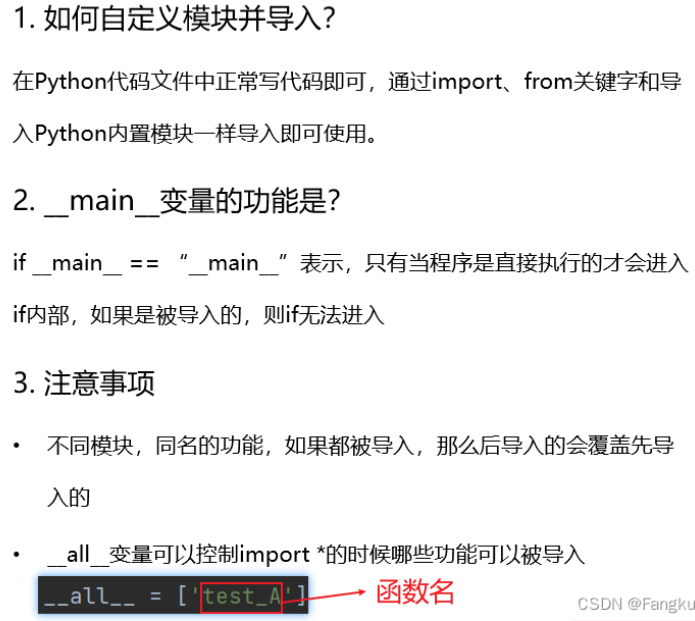
模块的导入

自定义模块
类和对象

构造方法
class student:
name = None
age = None
# 构造方法
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
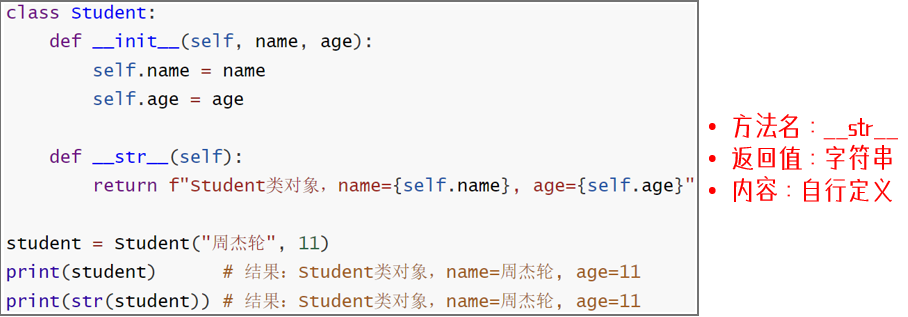
魔术方法
str方法
lt方法

le方法

eq方法

封装、继承和多态
由于Python是基于C语言开发的面向对象的语言,其封装、继承和多态与C语言有许多相似之处。
封装
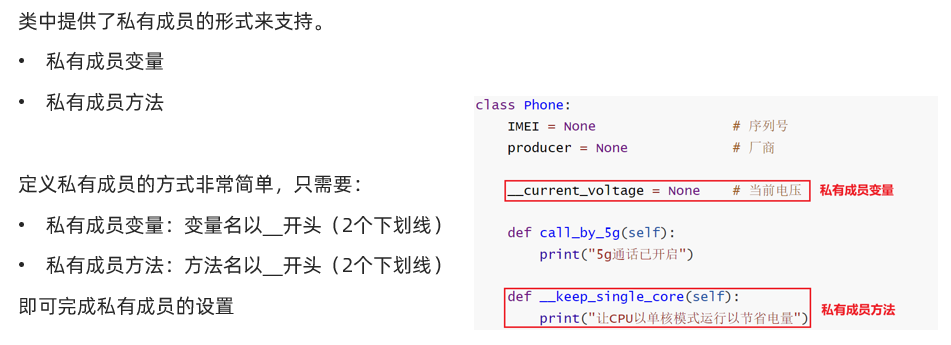

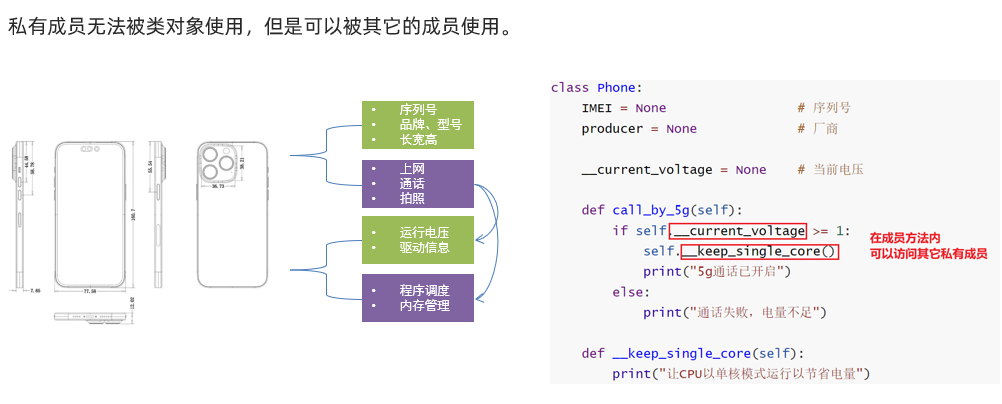
继承
继承的基础语法
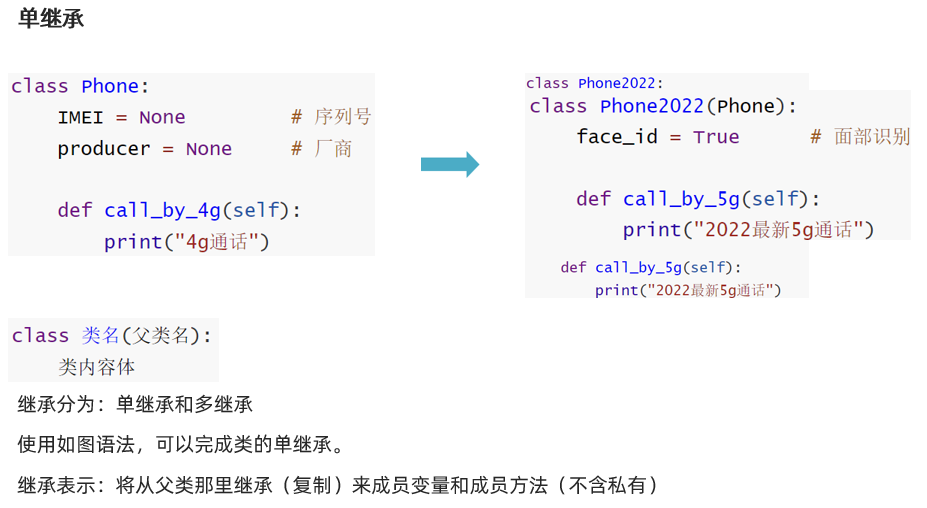
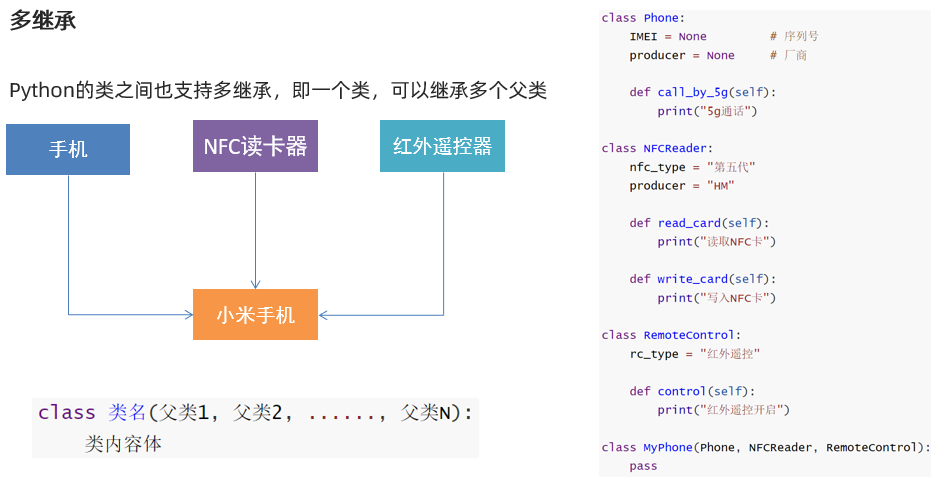
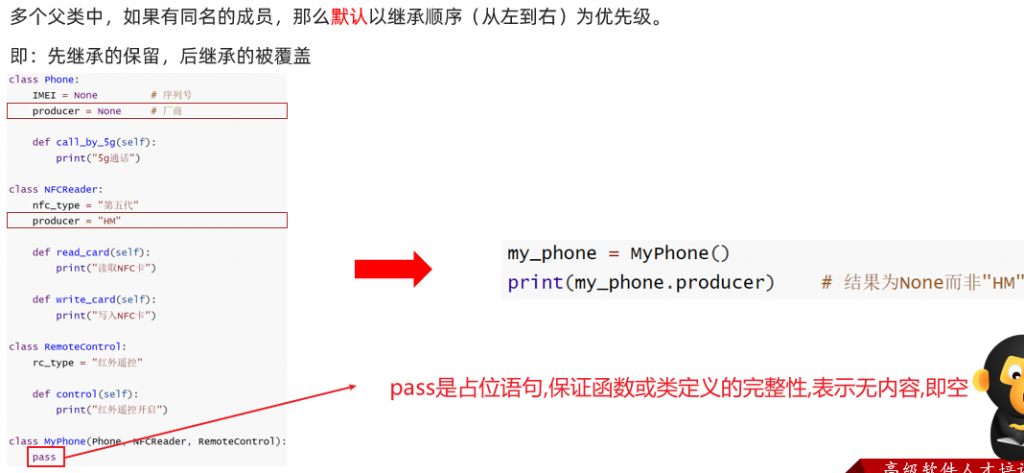
复写和使用父类成员

类型注解
变量的类型注解

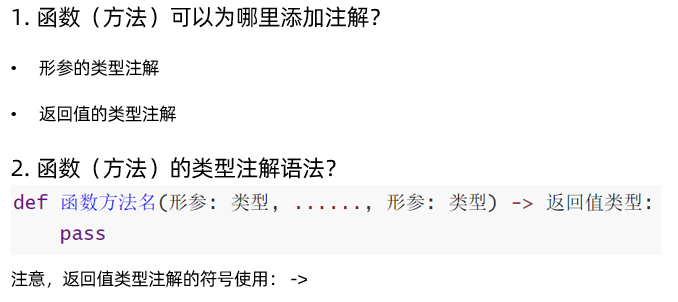
函数(方法)的类型注解
Union类型

多态



