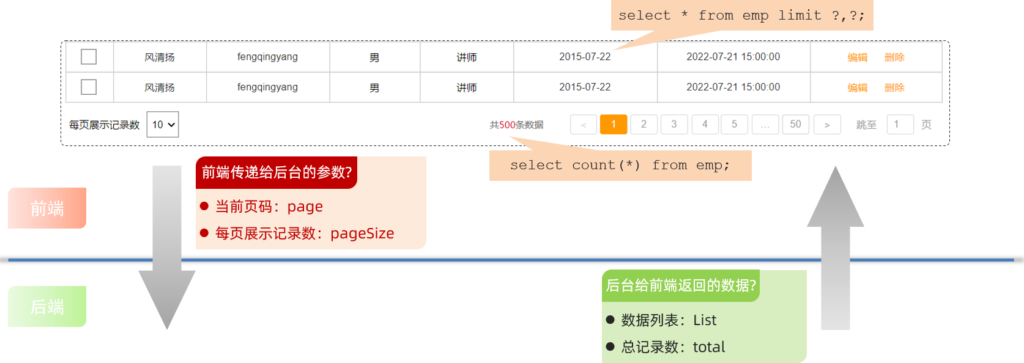
基础分页
需求分析
要想从数据库中进行分页查询,我们要使用LIMIT关键字,格式为:limit 开始索引 每页显示的条数
查询第1页数据的SQL语句是:
select * from emp limit 0,10;查询第2页数据的SQL语句是:
select * from emp limit 10,10;查询第3页的数据的SQL语句是:
select * from emp limit 20,10;观察以上SQL语句,发现: 开始索引一直在改变 , 每页显示条数是固定的
开始索引的计算公式: 开始索引 = (当前页码 – 1) * 每页显示条数
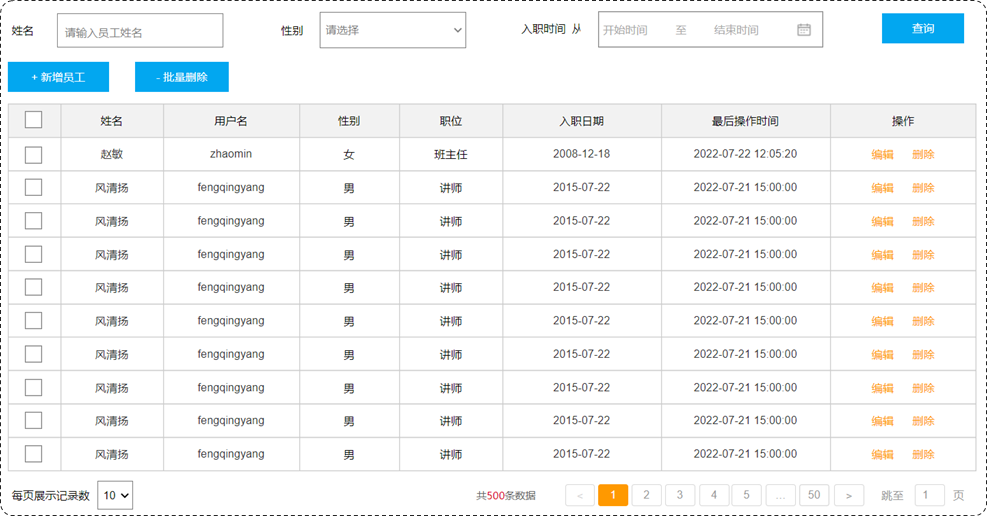
我们继续基于页面原型,继续分析,得出以下结论:
- 前端在请求服务端时,传递的参数
- 当前页码 page
- 每页显示条数 pageSize
- 后端需要响应什么数据给前端
- 所查询到的数据列表(存储到 List 集合中)
- 总记录数
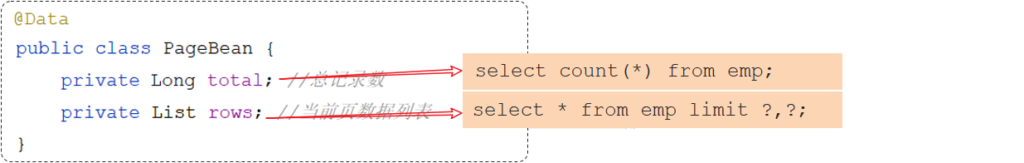
后台给前端返回的数据包含:List集合(数据列表)、total(总记录数),而这两部分我们通常封装到PageBean对象中,并将该对象转换为json格式的数据响应回给浏览器。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class PageBean {
private Long total; //总记录数
private List rows; //当前页数据列表
}思路分析

分页查询需要的数据,封装在PageBean对象中:
功能开发
通过查看接口文档:员工列表查询
- 请求路径:/emps
- 请求方式:GET
- 请求参数:跟随在请求路径后的参数字符串。 例:/emps?page=1&pageSize=10
- 响应数据:json格式
EmpController
import com.itheima.pojo.PageBean;
import com.itheima.pojo.Result;
import com.itheima.service.EmpService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
//条件分页查询
@GetMapping
public Result page(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") Integer pageSize) {
//记录日志
log.info("分页查询,参数:{},{}", page, pageSize);
//调用业务层分页查询功能
PageBean pageBean = empService.page(page, pageSize);
//响应
return Result.success(pageBean);
}
}@RequestParam(defaultValue=”默认值”) //设置请求参数默认值
EmpService
public interface EmpService {
/**
* 条件分页查询
* @param page 页码
* @param pageSize 每页展示记录数
* @return
*/
PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize);
}EmpServiceImpl
import com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper;
import com.itheima.pojo.Emp;
import com.itheima.pojo.PageBean;
import com.itheima.service.EmpService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private EmpMapper empMapper;
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize) {
//1、获取总记录数
Long count = empMapper.count();
//2、获取分页查询结果列表
Integer start = (page - 1) * pageSize; //计算起始索引 , 公式: (页码-1)*页大小
List<Emp> empList = empMapper.list(start, pageSize);
//3、封装PageBean对象
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(count , empList);
return pageBean;
}
}EmpMapper
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
//获取总记录数
@Select("select count(*) from emp")
public Long count();
//获取当前页的结果列表
@Select("select * from emp limit #{start}, #{pageSize}")
public List<Emp> list(Integer start, Integer pageSize);
}功能测试
功能开发完成后,重新启动项目,使用postman,发起GET请求:
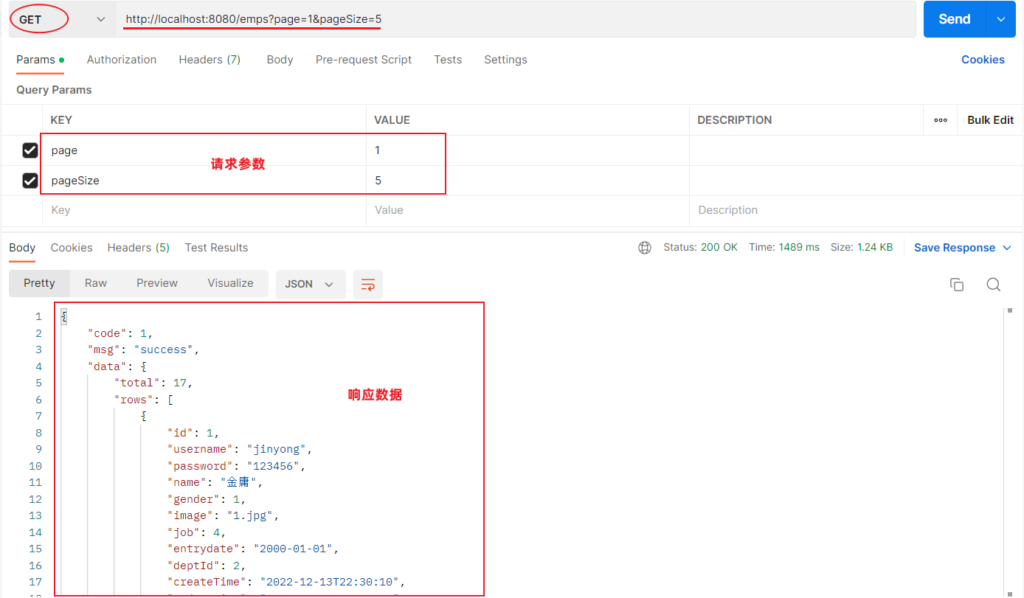
Mybatis分页插件
前面我们已经完成了基础的分页查询,会发现:分页查询功能编写起来比较繁琐。
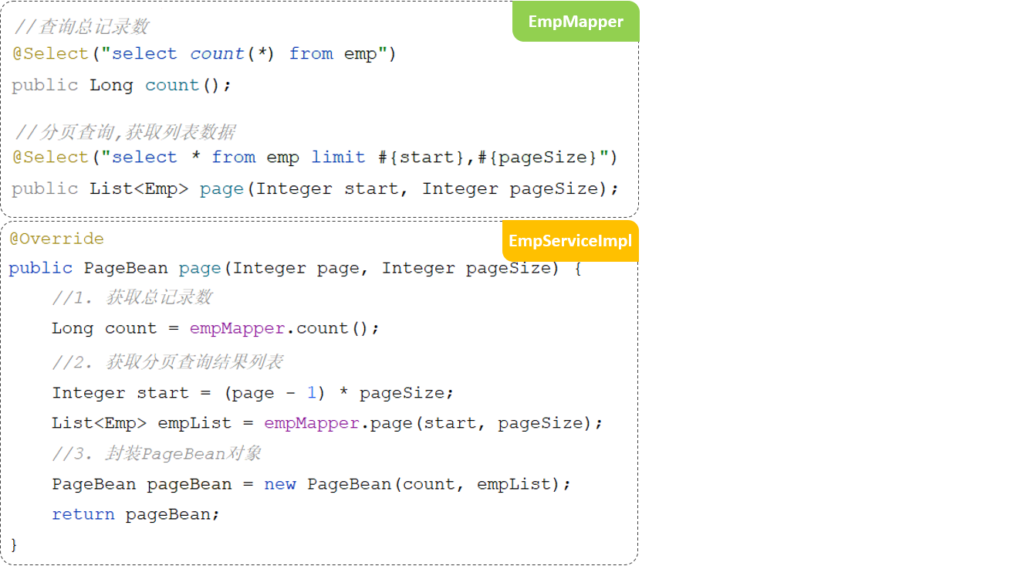
结论:原始方式的分页查询,存在着”步骤固定”、”代码频繁”的问题
解决方案:可以使用一些现成的分页插件完成。对于Mybatis来讲现在最主流的就是PageHelper。
PageHelper是Mybatis的一款功能强大、方便易用的分页插件,支持任何形式的单标、多表的分页查询。
官网:https://pagehelper.github.io/
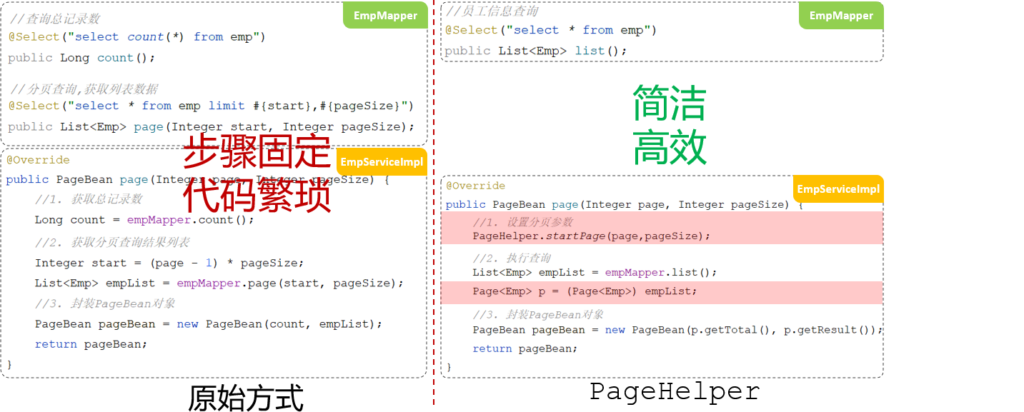
在执行empMapper.list()方法时,就是执行:select * from emp 语句,怎么能够实现分页操作呢?
分页插件帮我们完成了以下操作:
- 先获取到要执行的SQL语句:select * from emp
- 把SQL语句中的字段列表,变为:count(*)
- 执行SQL语句:select count(*) from emp //获取到总记录数
- 再对要执行的SQL语句:select * from emp 进行改造,在末尾添加 limit ? , ?
- 执行改造后的SQL语句:select * from emp limit ? , ?
代码实现
当使用了PageHelper分页插件进行分页,就无需再Mapper中进行手动分页了。 在Mapper中我们只需要进行正常的列表查询即可。在Service层中,调用Mapper的方法之前设置分页参数,在调用Mapper方法执行查询之后,解析分页结果,并将结果封装到PageBean对象中返回。
1、在pom.xml引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>2、EmpMapper
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
//获取当前页的结果列表
@Select("select * from emp")
public List<Emp> page(Integer start, Integer pageSize);
}3、EmpServiceImpl
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize) {
// 设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(page, pageSize);
// 执行分页查询
List<Emp> empList = empMapper.list();
// 获取分页结果 Page类由Mybatis提供
Page<Emp> p = (Page<Emp>) empList;
//封装PageBean getTotal()获取总记录数 getResult()获取结果列表
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(p.getTotal(), p.getResult());
return pageBean;
}PageHelper.startPage()方法的作用是将接下来的一条SQL查询语句进行分页处理,查询结果会被自动封装成Page类型对象,其中包含了分页需要的全部信息,包括当前页码、每页显示数量、总记录数、总页数等。
测试
功能开发完成后,我们重启项目工程,打开postman,发起GET请求,访问 :http://localhost:8080/emps?page=1&pageSize=5
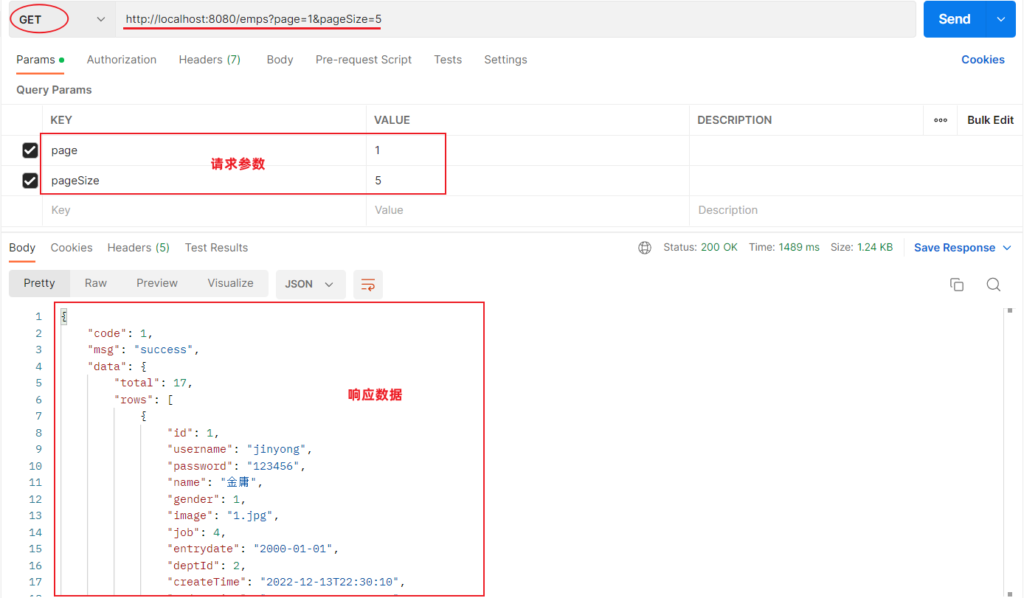
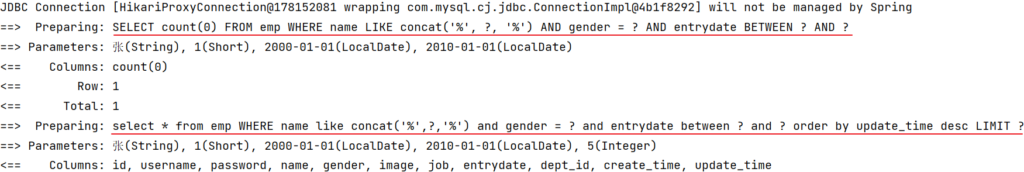
后端程序SQL输出:
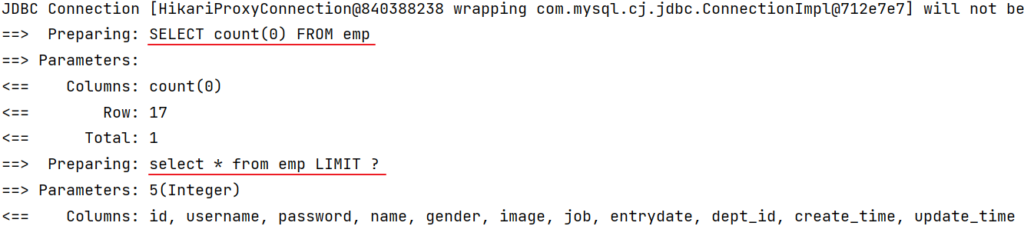
分页查询(带条件)
需求分析
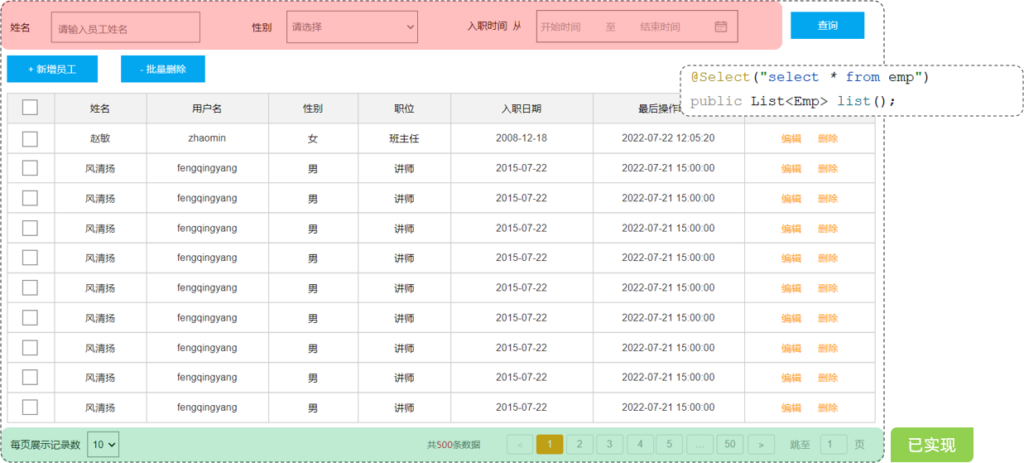
通过员工管理的页面原型我们可以看到,员工列表页面的查询,不仅仅需要考虑分页,还需要考虑查询条件。 分页查询我们已经实现了,接下来,我们需要考虑在分页查询的基础上,再加上查询条件。
我们看到页面原型及需求中描述,搜索栏的搜索条件有三个,分别是:
- 姓名:模糊匹配
- 性别:精确匹配
- 入职日期:范围匹配
select *
from emp
where
name like concat('%','张','%') -- 条件1:根据姓名模糊匹配
and gender = 1 -- 条件2:根据性别精确匹配
and entrydate = between '2000-01-01' and '2010-01-01' -- 条件3:根据入职日期范围匹配
order by update_time desc;而且上述的三个条件,都是可以传递,也可以不传递的,也就是动态的。 我们需要使用前面学习的Mybatis中的动态SQL 。
思路分析

功能开发
通过查看接口文档:员工列表查询
- 请求路径:/emps
- 请求方式:GET
- 请求参数:
| 参数名称 | 是否必须 | 示例 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | 否 | 张 | 姓名 |
| gender | 否 | 1 | 性别 , 1 男 , 2 女 |
| begin | 否 | 2010-01-01 | 范围匹配的开始时间(入职日期) |
| end | 否 | 2020-01-01 | 范围匹配的结束时间(入职日期) |
| page | 是 | 1 | 分页查询的页码,如果未指定,默认为1 |
| pageSize | 是 | 10 | 分页查询的每页记录数,如果未指定,默认为10 |
在原有分页查询的代码基础上进行改造:
EmpController
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
//条件分页查询
@GetMapping
public Result page(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") Integer pageSize,
String name, Short gender,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate begin,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") LocalDate end) {
//记录日志
log.info("分页查询,参数:{},{},{},{},{},{}", page, pageSize,name, gender, begin, end);
//调用业务层分页查询功能
PageBean pageBean = empService.page(page, pageSize, name, gender, begin, end);
//响应
return Result.success(pageBean);
}
}EmpService
public interface EmpService {
/**
* 条件分页查询
* @param page 页码
* @param pageSize 每页展示记录数
* @param name 姓名
* @param gender 性别
* @param begin 开始时间
* @param end 结束时间
* @return
*/
PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize, String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
}EmpServiceImpl
@Slf4j
@Service
public class EmpServiceImpl implements EmpService {
@Autowired
private EmpMapper empMapper;
@Override
public PageBean page(Integer page, Integer pageSize, String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) {
//设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(page, pageSize);
//执行条件分页查询
List<Emp> empList = empMapper.list(name, gender, begin, end);
//获取查询结果
Page<Emp> p = (Page<Emp>) empList;
//封装PageBean
PageBean pageBean = new PageBean(p.getTotal(), p.getResult());
return pageBean;
}
}EmpMapper
@Mapper
public interface EmpMapper {
//获取当前页的结果列表
public List<Emp> list(String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
}EmpMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper">
<!-- 条件分页查询 -->
<select id="list" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Emp">
select * from emp
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
and gender = #{gender}
</if>
<if test="begin != null and end != null">
and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
</if>
</where>
order by update_time desc
</select>
</mapper>功能测试
功能开发完成后,重启项目工程,打开postman,发起GET请求:
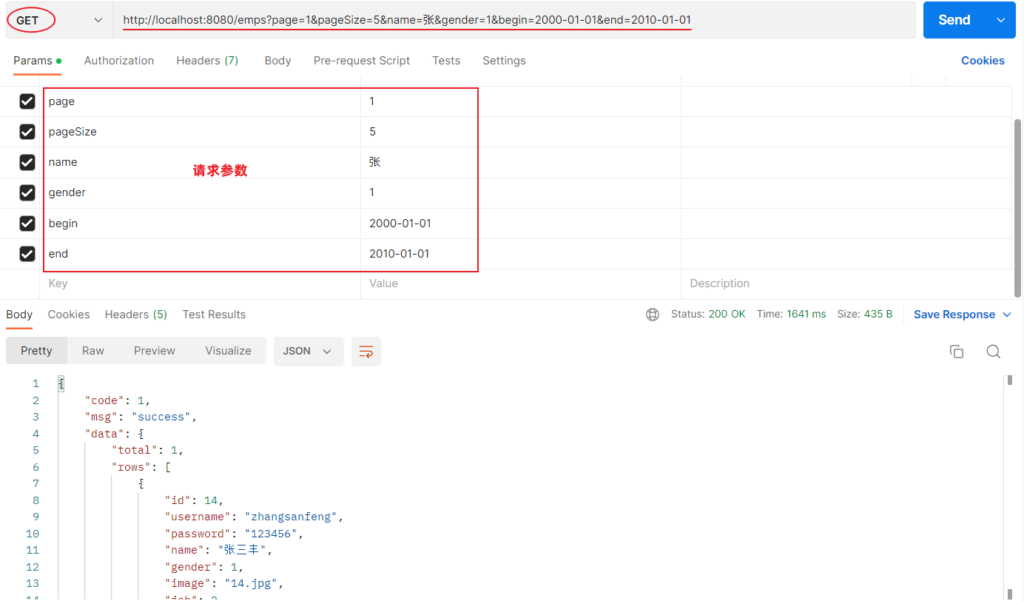
控制台SQL语句: